Muscle Loss Prevention: How to Avoid Muscle Loss and Preserve Your Health
Muscle loss prevention is essential for maintaining health, especially as we age. Muscle loss directly affects mobility, strength, and quality of life. Understanding the causes and prevention strategies is the first step toward healthy and active aging.
What is Muscle Loss and Why Does It Occur
Muscle loss, or sarcopenia, is the progressive reduction of skeletal muscle mass. This process can begin as early as age 30, intensifying over time, especially without proper care. Muscle loss prevention starts with understanding these root causes.
Aging and Sarcopenia
Aging reduces anabolic hormones like testosterone and growth hormone. This contributes to the natural decline in muscle mass, making muscle loss prevention more difficult without intervention.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Physical inactivity is one of the leading causes of muscle loss. Muscles need regular stimulation to maintain size and strength — a core principle in muscle loss prevention.
Poor Nutrition and Protein Deficiency
A protein-deficient diet limits the body’s ability to synthesize muscle tissue. Nutritional awareness is a pillar of effective muscle loss prevention.
Diseases and Clinical Conditions
Chronic illnesses like diabetes and cancer can accelerate muscle loss. Medical support is often necessary for comprehensive muscle loss prevention in such cases.
Figure: Muscle Loss Prevention – 4 Key Pillars
Symptoms and Signs of Muscle Loss
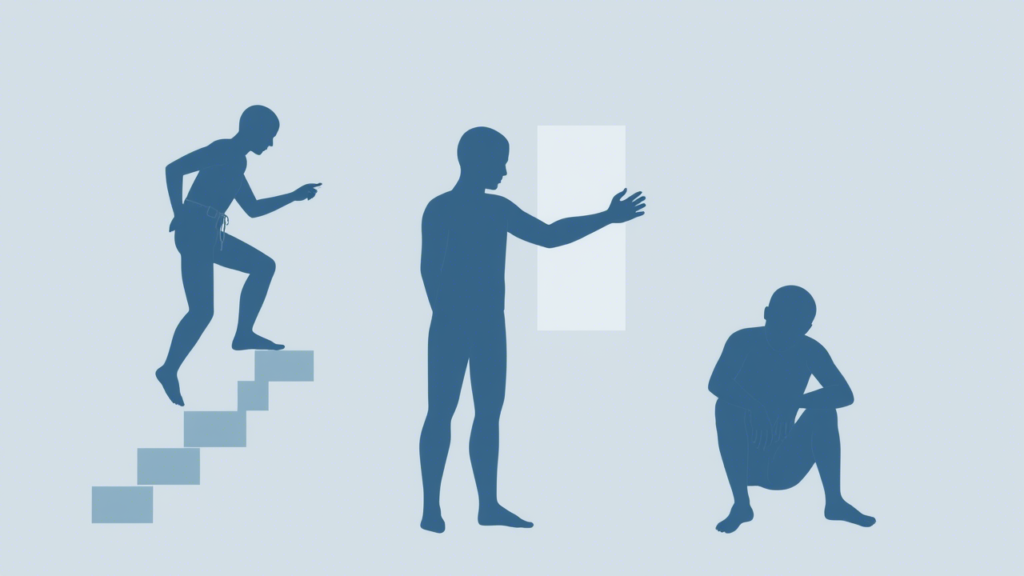

Early detection is critical for muscle loss prevention. Recognizing the symptoms allows quicker action to protect muscle mass and health.
Constant Muscle Weakness
Difficulty with everyday tasks, such as lifting light objects, is often a sign of muscle deterioration.
Reduced Physical Endurance
Fatigue after minimal effort could indicate decreased muscle function — a key concern for muscle loss prevention.
Visible Changes in the Body
Noticeable thinning in limbs often reflects loss of muscle mass.
Figure: Recognizing symptoms of muscle loss
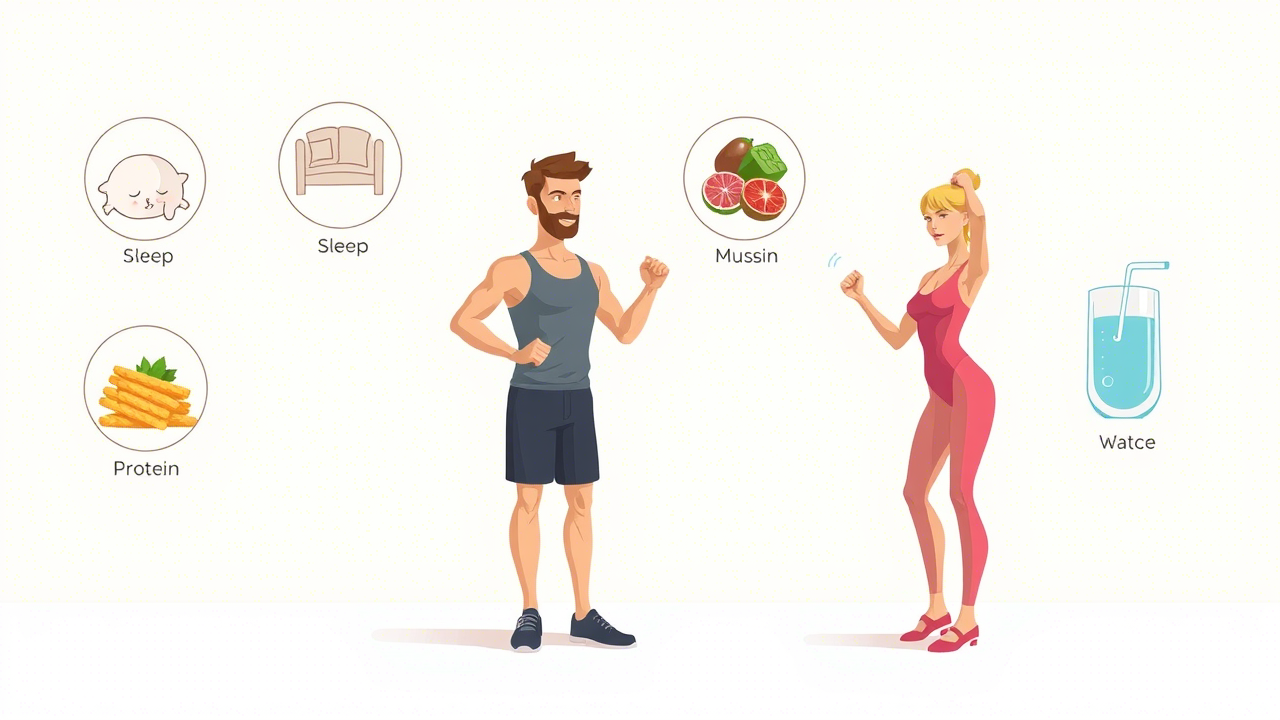
Muscle Loss Prevention Strategies You Can Apply
Protein-Rich Diet
Eat high-quality protein at every meal. Foods like eggs, lean meats, and legumes help your body rebuild and preserve muscle mass — central to muscle loss prevention.
Regular Strength Training
Resistance exercise maintains and increases muscle volume. It’s one of the most direct methods of muscle loss prevention.
Quality Sleep and Recovery
Rest is when muscle repair happens. Proper sleep is a non-negotiable part of muscle loss prevention.
Hydration and Hormonal Balance
Staying hydrated and keeping hormones in check supports metabolism and muscle function — aiding muscle loss prevention.
Links Recomendados
🛌 Descubra quais alimentos podem melhorar seu sono e contribuir para a recuperação muscular:
👉 Alimentos que ajudam você a dormir melhor
🌙 Veja dicas práticas para melhorar a qualidade do seu sono e potencializar a prevenção da perda muscular:
👉 Como melhorar a qualidade do sono
Muscle Loss Prevention and Reversal: Treatments and Approaches
Nutritional Supplementation
Whey protein, creatine, and BCAAs can help combat muscle deterioration. Use them under professional guidance to support muscle loss prevention.
Physical Therapy and Guided Exercises
Fisiotherapy is ideal for people already showing signs of sarcopenia. Customized exercises accelerate muscle loss prevention and recovery.
Medical Monitoring
Endocrinologists and geriatricians can help identify and address underlying issues related to muscle loss.
Everyday Habits for Effective Muscle Loss Prevention
- Train 2–4 times per week with resistance exercises
- Eat complete proteins throughout the day
- Sleep at least 7 hours per night
- Hydrate and manage stress
- Schedule regular health check-ups
Conclusion: Commit to Muscle Loss Prevention Today
Muscle loss prevention requires consistency, awareness, and a proactive mindset. With the right nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle habits, you can preserve muscle mass and enjoy strength and vitality at any age.
🔗 For a deeper understanding of muscle atrophy and clinical approaches, visit:
👉 Muscle Atrophy – Wikipedia


No responses yet