Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Identify the Symptoms and Learn How to Prevent It
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a silent, progressive condition that is often overlooked. Its symptoms can develop slowly, often mistaken for stress, aging, or other illnesses. However, this deficiency can cause serious and even permanent effects, especially on the nervous system.
In this article, you will understand the main signs of vitamin B12 deficiency, its causes, how to diagnose and treat it, and how to prevent this condition effectively.
What Is Vitamin B12 and Why Is It Important for the Body?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential water-soluble nutrient from the B-complex family. It plays key roles in several vital functions:
Production of red blood cells
DNA synthesis
Maintenance of brain and nerve health
Energy and protein metabolism
Its deficiency can directly affect the blood, brain, and nervous system.
Common Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can arise from multiple causes. Understanding these factors is essential for prevention.
Poor dietary intake
Vitamin B12 is found only in animal-derived foods such as meat, milk, eggs, and cheese. Strict vegan or vegetarian diets require consistent supplementation to avoid deficiency.
Gastrointestinal malabsorption
Even with proper nutrition, the body may fail to absorb B12 due to:
Celiac disease
Atrophic gastritis
Irritable bowel syndrome
Bariatric surgery
These conditions impair the production of intrinsic factor, which is essential for B12 absorption.
Long-term use of certain medications
Some medications interfere with B12 absorption when used over time, such as:
Metformin
Proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, pantoprazole)
Anticonvulsants
Main Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency presents a wide range of symptoms, often worsening over time. The most frequent include:
Persistent fatigue and low energy
Cobalamin is essential for red blood cell formation. A deficiency reduces tissue oxygenation, causing chronic fatigue, even after rest.
Numbness and tingling sensations
Vitamin B12 is critical for maintaining the myelin sheath that protects nerves. A lack of B12 can lead to tingling, numbness, and electric shock-like sensations in the limbs.
Memory loss and poor concentration
B12 deficiency can affect cognitive functions, leading to:
Difficulty focusing
Forgetting simple tasks
Reduced learning ability
Mental confusion
In older adults, it may resemble early-stage dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
Pale or yellowish skin (jaundice)
B12 deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia, which leads to pale skin. In some cases, excess bilirubin causes yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Mood changes
Low B12 levels may contribute to mental health symptoms such as:
Mild to moderate depression
Irritability
Anxiety
Several studies link B12 deficiency to an increased risk of mood disorders.
Lesser-Known Signs of B12 Deficiency
Some symptoms are subtle or misattributed to other causes. These include:
Glossitis (red, swollen, and painful tongue)
Loss of appetite
Altered taste perception
Dizziness and balance issues
Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
These signs may appear independently and should be evaluated when persistent.
Risk Groups for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Certain populations are more likely to develop B12 deficiency, including:
Adults over 60 years old
Pregnant and breastfeeding women
Vegetarians and vegans
Individuals with gastrointestinal disorders
Post-bariatric surgery patients
Long-term users of metformin or proton pump inhibitors
Routine blood tests are recommended for these groups.
The Link Between B12 Deficiency and Chronic Diseases
Research shows that vitamin B12 deficiency can worsen or accelerate chronic disease progression. Notable associations include:
Cardiovascular disease: B12 regulates homocysteine levels, a pro-inflammatory amino acid linked to heart attack and stroke risk.
Type 2 diabetes: Long-term metformin use may lead to B12 deficiency.
Dementia: B12 deficiency is associated with cognitive decline over time.
Maintaining proper B12 levels may help prevent or mitigate complications of these conditions.
Diagnosing Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Proper diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and specific lab tests:
Serum B12 level: Levels below 200 pg/mL typically indicate deficiency.
Methylmalonic acid (MMA): A sensitive marker when diagnosis is unclear.
Plasma homocysteine: High levels suggest metabolic disturbance.
Complete blood count: May reveal megaloblastic anemia.
Early detection is critical to avoid irreversible damage.
Treatment for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Treatment depends on the severity and underlying cause of the deficiency:
Oral supplements: Effective for mild cases, especially those caused by diet.
Intramuscular injections: Recommended for malabsorption or severe deficiency.
Dietary adjustments: Essential to prevent relapse.
Treatment frequency may vary from weekly to monthly, as advised by a healthcare provider. Physical symptoms improve within weeks, while neurological recovery may take longer.
How to Prevent Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Prevention is simple and highly effective. Follow these strategies:
Consume B12-rich foods: beef, liver, eggs, dairy, poultry, fish.
Use supplements: essential for vegans, vegetarians, and at-risk groups.
Annual check-ups: include B12 tests in routine blood work.
Avoid self-medication: long-term drug use should be monitored by a physician.
Foods Rich in Vitamin B12
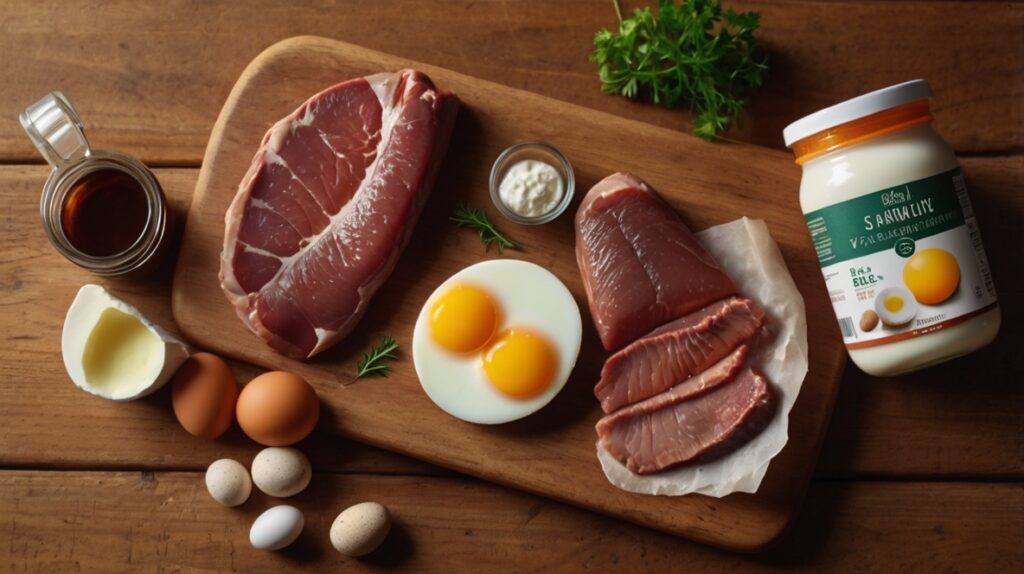

Incorporate these foods into your diet:
Beef liver
Boiled eggs
Sardines and tuna
Whole milk
Parmesan cheese
Grilled chicken
Natural yogurt
Avoid overcooking, which can destroy part of the vitamin content.
Improve Your Metabolism Naturally
Want to boost your metabolism and increase your energy levels? Learn how healthy habits can improve both physical and mental performance:
➡️ How to Boost Metabolism Naturally
Reduce Inflammation That Worsens Symptoms
Chronic inflammation can aggravate symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency. Learn how to reduce it naturally and safely:
➡️ How to Reduce Inflammation Naturally
Learn More About the Effects and Treatment of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
For more in-depth, medically reviewed information about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency, visit the Cleveland Clinic:
➡️ Cleveland Clinic – Vitamin B12 Deficiency

No responses yet